A breakthrough in mechanistic interpretability!
MECHANISTIC INTERPRETABILITY
The Geometry of Concepts. Sparse Autoencoder Feature Structure. Tegmark et al.
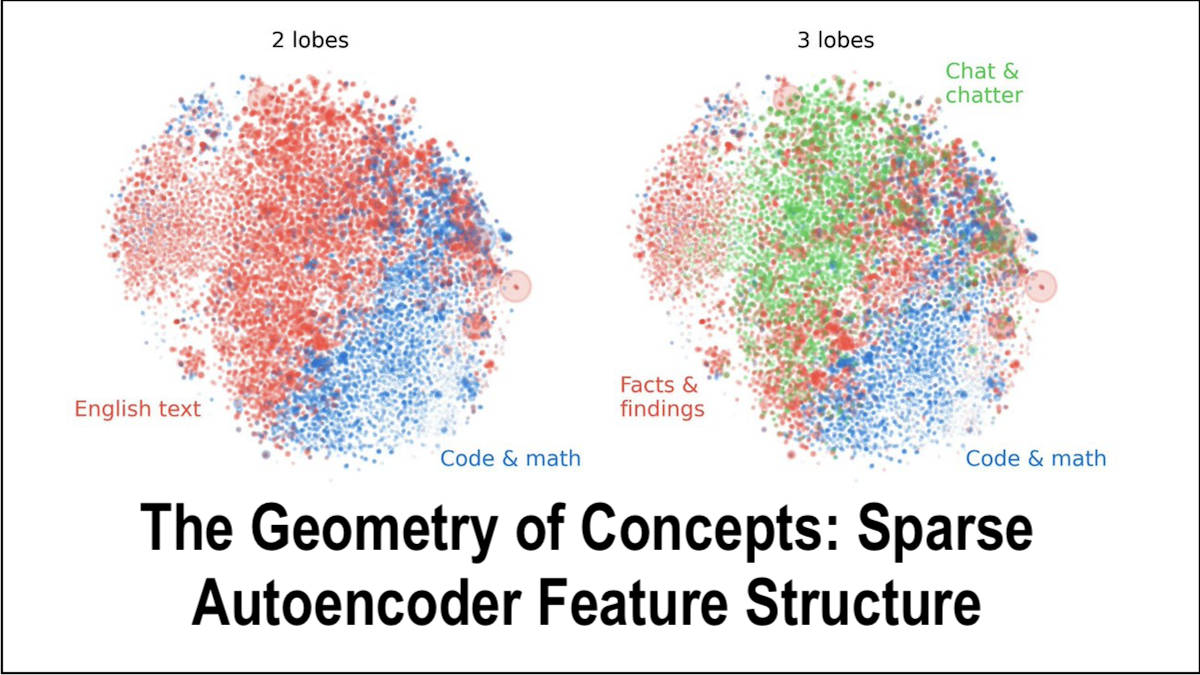
Abstract. Sparse autoencoders have recently produced dictionaries of high-dimensional vectors corresponding to the universe of concepts represented by large language models. We find that this concept universe has interesting structure at three levels: 1) The “atomic” small-scale structure contains “crystals” whose faces are parallelograms or trapezoids, generalizing well-known examples such as (man:woman::king:queen). We find that the quality of such parallelograms and associated function vectors improves greatly when projecting out global distractor directions such as word length, which is efficiently done with linear discriminant analysis. 2) The “brain” intermediate-scale structure has significant spatial modularity; for example, math and code features form a “lobe” akin to functional lobes seen in neural fMRI images. We quantify the spatial locality of these lobes with multiple metrics and find that clusters of co-occurring features, at coarse enough scale, also cluster together spatially far more than one would expect if feature geometry were random. 3) The “galaxy” scale large-scale structure of the feature point cloud is not isotropic, but instead has a power law of eigenvalues with steepest slope in middle layers. We also quantify how the clustering entropy depends on the layer.
We found that concepts in an AI brain (nerdspeak: “LLM SAE features”) that activate close together in time are also close together in (“activation”) space, akin to lobes in a biological brain: https://t.co/CfanjP27n5
— Max Tegmark (@tegmark) November 1, 2024
Our new AI paper reveals surprising geometric structure in the LLM-learned concepts: 1) They form brain-like “lobes”, 2) they form “semantic crystals” much more precise than it first seems, and 3) the concept cloud is more fractal than round: https://t.co/Mev7bGUe09
— Max Tegmark (@tegmark) October 29, 2024